Verge.swift
_ 更简单的单链数据流获取方式 _
_ 支持并发处理 _
https://vergegroup.github.io/Verge/documentation/verge/
新闻
仍在开发中 下一个Verge实现已经开始。
它使用了swift-concurrency
需求
- Swift 5.5 +
- @available(iOS 10, macOS 10.13, tvOS 10, watchOS 3)
- UIKit
- SwiftUI
Verge不是Flux,它是store-pattern且功能强大。
Verge是一个高性能的基于store模式的iOS状态管理库。
请访问网站:https://vergegroup.org
什么是store模式
“store-pattern”一词在Vue.js文档中使用,介绍了我们如何在多个组件之间管理状态。
使用Verge的项目
我们欢迎在此发布由Verge提供动力的应用!
请通过pull请求提交
最小使用示例 - 在UIView - UIViewController
状态管理无处不在,你可以放置一个store并开始状态管理。
final class CropViewController: UIViewController {
private struct State: Equatable {
var isSelectingAspectRatio = false
}
private let store: Store<State, Never> = .init(initialState: .init())
private var subscriptions = Set<VergeAnyCancellable>()
override public func viewDidLoad() {
store.sinkState { [weak self] state in
guard let self = self else { return }
state.ifChanged(\.isSelectingAspectRatio) { value in
//
}
}
.store(in: &subscriptions)
}
func showAspectRatioSelection() {
store.commit {
$0.isSelectingAspectRatio = true
}
}
func hideAspectRatioSelection() {
store.commit {
$0.isSelectingAspectRatio = false
}
}
}高级使用示例 - UIKit / SwiftUI
创建视图模型(即store)
final class MyViewModel: StoreComponentType {
/// 💡 The state declaration can be aslo inner-type.
/// As possible adding Equatable for better performance.
struct State: Equatable {
struct NestedState: Equatable {
...
}
var name: String = ""
var count: Int = 0
var nested: NestedState = .init()
}
/// 💡 This is basically a template statement. You might have something type of `Store`.
let store: DefaultStore = .init(initialState: .init())
// MARK: - ✅ These are actions as well as writing methods.
func myAction() {
// 💥 Mutating a state
commit {
$0.name = "Hello, Verge"
}
}
func incrementAsync() {
/**
💥 Asynchronously mutating.
Verge just provides thread-safety.
We should manage operations in the Action.
*/
DispatchQueue.global().async {
commit {
// We must finish here synchronously - here is a critical session.
$0.count += 1
}
}
}
}在SwiftUI
struct MyView: View {
let store: MyViewModel
var body: some View {
// ✅ Uses `StateReader` to read the state this clarifies where components need the state.
StateReader(store) { state in
Text(state.name)
Button(action: {
self.store.myAction()
}) {
Text("Action")
}
}
}
}StateReader支持像下面这样推导状态的一部分。
StateReader(store.derived(.map(\.nested))) { state in
...
}
🤲 Verge在SwiftUI中尚未积累足够经验。请通过讨论或问题告诉我们您改善Verge在使用SwiftUI的想法!(在讨论或问题中)
在UIKit
与视图(或视图控制器)的绑定
final class MyViewController: UIViewController {
let viewModel: MyViewModel
...
var cancellable: VergeAnyCancellable?
init(viewModel: MyViewModel) {
self.viewModel = viewModel
// ✅ Start subscribing the state.
self.cancellable = viewModel.sinkState { [weak self] (state: Changes<MyViewModel.State>) in
self?.update(state: state)
}
}
/**
Actually we don't need to create such as this method, but here is for better clarity in this document.
*/
private func update(state: Changes<MyViewModel.State>) {
/**
💡 `Changes` is a reference-type, but it's immutable.
And so can not subscribe.
Why is it a reference-type? Because it's for reducing copying cost.
It can detect difference with previous value with it contains a previous value.
Which is using `.ifChanged` or `.takeIfChanged`.
*/
/// 🥤 An example that setting the value if the target value has updated.
state.ifChanged(\.name) { (name) in
// ✅ `name` has changed! Update the text.
nameLabel.text = name
}
/// 🥤 An example that composing as a tuple to behave like RxSwift's combine latest.
state.ifChanged({ ($0.name, $0.count) }, ==) { (name, count) in
/**
Receives every time the tuple differs from the previous one.
This means it changes when anyone in the tuple changed
*/
nameLabel.text = name
countLabel.text = age.description
}
...
}
}支持与RxSwift集成
Verge支持与RxSwift集成,可以创建State和Activity的流。要启用它,请安装VergeRx模块。
Flux库之间的差异
‘store-pattern’是Flux的核心概念。Flux在‘store-pattern’的基础上受到了多重约束规则的指导。
这意味着我们可以在不使用Action、Mutation有效载荷值的情况下开始使用Flux。
// ✌️ no needs to use.
enum Action {
case increment
case decrement
}这种声明可能需要很大的实现成本,才能开始使用Flux。
Verge没有这些规则,因此当更新状态时,我们可以这样做。
// 🤞 just like this
extension MyStore {
func increment() {
commit {
$0.count += 1
}
}
}
let store: MyStore
store.increment()它可以容易地开始。
当然,我们可以在Verge原语层上创建一个层次结构来管理严格的作用和mutation有效载荷。
因为‘store-pattern’是Flux的核心概念。
--
动机
Verge关注实际场景的应用
最近,我们可以说单向数据流是一种流行的架构,如Flux。
store-pattern(Flux)架构是否具有良好的性能?
这取决于。性能的最差取决于如何使用它。
然而,在大多数情况下,我们不知道我们创建的应用将如何增长和扩展。
在应用程序扩缩时,由于复杂性增加,性能可能会下降。
为保持性能,我们需要采用多种方法进行调优。
考虑到性能从一开始就需要时间。
这可能导致我们使用 flux 架构感到烦恼。
Verge专为从小规模使用并支持扩展而设计。
快速设置 Verge,并在需要时对其进行调优。
Verge会自动进行调优,并从 Xcode 的文档中显示导致性能不佳的因素。
例如,Verge提供了以下内容来提高性能。
- 派生(类似于facebookexperimental/Recoil's Selector)
- ORM
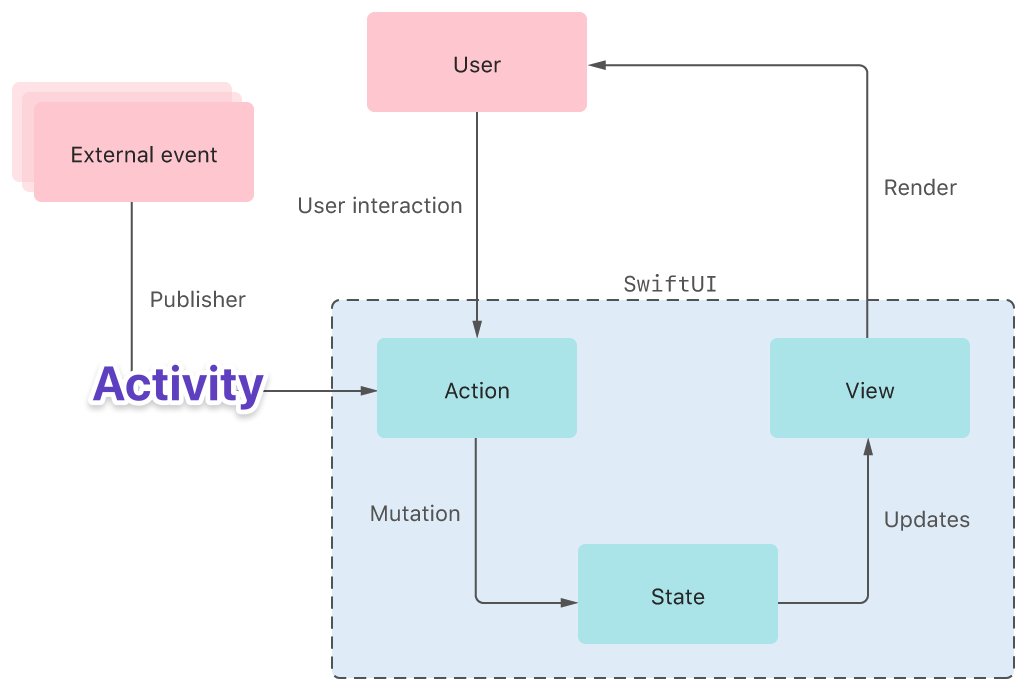
支持易变事件
我们将事件用作 Activity,它不会存储在状态中。
这个概念将帮助我们描述客户端应用程序中难以描述为状态的内容。
安装
CocoaPods
Verge(核心模块)
pod 'Verge/Store'VergeORM
pod 'Verge/ORM'VergeRx
pod 'Verge/Rx'在 Podspec 中,这些使用了 subspecs 进行分割。
安装后,这些将合并为单个模块,作为 Verge。
要在代码中使用 Verge,请按以下方式定义导入声明。
import VergeSwiftPM
Verge 还支持 SwiftPM。
问题
请随意提问此库相关的问题!
我会在Twitter上更快地回复你。
日语提问也没有问题
从Twitter上可以获得更快的回复
示例应用
此仓库中有几个示例应用位于Demo目录中。我们正在寻找您的示例应用以在此列出!请在Issue中告诉我们!
感谢
作者
许可证
Verge是在MIT许可证下发布的。