TaskQueue
目录
简介
TaskQueue 是一个 Swift 库,允许您一次调度任务,然后让队列以同步方式执行它们。TaskQueue 的好处是您可以在事先决定每个任务应该在哪个 GCD 队列中执行,并让 TaskQueue 在执行过程中切换队列。
即使您的任务异步,如获取位置、下载文件等,TaskQueue 也会在继续下一个任务之前等待它们完成。
最后但同样重要的是,您对队列有完整的流程控制,根据您在任务中执行工作的结果,您可以跳过下一个任务,终止队列,或直接跳转到队列完成。您还可以暂停、恢复和停止队列。
安装
CocoaPods
CocoaPods 是一个为 Cocoa 项目提供依赖管理的工具。
如果你还没有安装 Cocoapods宝石,请运行以下命令
$ gem install cocoapods要使用 CocoaPods 将 TaskQueue 集成到您的 Xcode 项目中,请在您的 Podfile 中指定它
pod 'TaskQueue'然后,运行以下命令
$ pod install如果您发现运行 pod install 时没有安装最新版本,请尝试运行
$ pod cache clean
$ pod repo update TaskQueue
$ pod install另外,您还需要确保在您的 Podfile.lock 文件中没有将 TaskQueue 锁定到旧版本。
Carthage
Carthage 是一个分布式依赖管理工具,可以自动化向您的 Cocoa 应用程序添加框架的过程。
您可以使用以下命令使用 Homebrew 安装 Carthage
$ brew update
$ brew install carthage要使用 Carthage 将 TaskQueue 集成到您的 Xcode 项目中,请在您的 Cartfile 中指定它
github "icanzilb/TaskQueue"
简单示例
同步任务
这是在 Swift 中使用 TaskQueue 的最简单方法
let queue = TaskQueue()
queue.tasks +=~ {
... time consuming task on a background queue...
}
queue.tasks +=! {
... update UI on main queue ...
}
queue.run()TaskQueue 将依次执行任务,等待每个任务完成后再执行下一个。通过使用运算符 +=~ 和 +=!,您可以轻松设置任务应在后台还是主队列中执行。
异步任务
当然更有趣的是,当您需要在任务的后台执行一些异步工作。然后,您可以在任务中获取next参数,并在异步工作完成时调用它
let queue = TaskQueue()
queue.tasks +=~ { result, next in
var url = URL(string: "http://jsonmodel.com")
URLSession.shared.dataTask(with: url,
completionHandler: { _, _, _ in
// process the response
next(nil)
})
}
queue.tasks +=! {
print("execute next task after network call is finished")
}
queue.run {
print("finished")
}以上示例中有几点需要强调
-
第一个任务闭包得到两个参数:
result是前一个任务的结果(在第一个任务的情况下是nil)以及next。当您的异步任务执行完毕时,你需要调用这个next。 -
任务编号2只有在您在前一个任务中调用
next()后才会开始 -
函数
run也可以接受一个闭包作为参数——如果传入了一个闭包,它将在所有其他任务完成后始终执行。
串行和并发任务
默认情况下,TaskQueue按顺序执行其任务,换句话说,队列一次最多只有一个正在执行的任务。
然而,您可以允许同时执行一定数量的任务(例如,如果您需要从网站上下载一组图像文件)。要做到这一点,只需增加正在执行的任务数量,队列将自动开始并行执行任务。例如
queue.maximumNumberOfActiveTasks = 10这将使队列同时执行多达10个任务。
注意:一旦允许同时执行多个任务,将应用某些限制:您无法调用retry(),也无法将结果从一项任务传递到另一项任务。
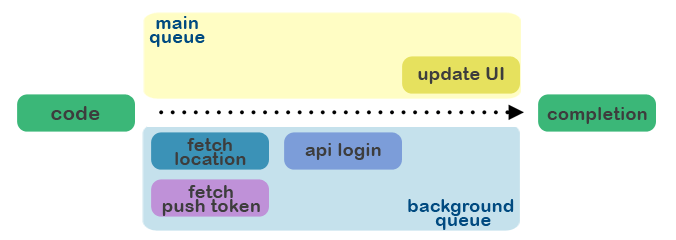
GCD队列控制
您想在后台运行一些重量级任务,然后切换到主队列更新您的应用程序UI?很简单。请查阅以下示例,它展示了使用TaskQueue的GCD队列控制。
let queue = TaskQueue()
//
// "+=" adds a task to be executed on the current queue
//
queue.tasks += {
// update the UI
}
//
// "+=~" adds a task to be executed in the background, e.g. low prio queue
// "~" stands for so~so priority
//
queue.tasks +=~ {
// do heavy work
}
//
// "+=!" adds a task to be executed on the main queue
// "!" stands for High! priority
//
queue.tasks +=! {
// update the UI again
}
// to start the queue on the current GCD queue
queue.run()详细示例
let queue = TaskQueue()
//
// Simple sync task, just prints to console
//
queue.tasks += {
print("====== tasks ======")
print("task #1: run")
}
//
// A task, which can be asynchronious because it gets
// result and next params and can call next() when ready
// with async work to tell the queue to continue running
//
queue.tasks += { result, next in
print("task #2: begin")
delay(seconds: 2) {
print("task #2: end")
next(nil)
}
}
//
// A task which retries the same task over and over again
// until it succeeds (i.e. util when you make network calls)
// NB! Important to capture **queue** as weak to prevent
// memory leaks!
//
var cnt = 1
queue.tasks += { [weak queue] result, next in
print("task #3: try #\(cnt)")
cnt += 1
if cnt > 3 {
next(nil)
} else {
queue!.retry(delay: 1)
}
}
//
// This task skips the next task in queue
// (no capture cycle here)
//
queue.tasks += {
print("task #4: run")
print("task #4: will skip next task")
queue.skip()
}
queue.tasks += {
print("task #5: run")
}
//
// This task removes all remaining tasks in the queue
// i.e. util when an operation fails and the rest of the queueud
// tasks don't make sense anymore
// NB: This does not remove the completions added
//
queue.tasks += {
print("task #6: run")
print("task #6: will append one more completion")
queue.run { _ in
print("completion: appended completion run")
}
print("task #6: will skip all remaining tasks")
queue.removeAll()
}
queue.tasks += {
print("task #7: run")
}
//
// This either runs or resumes the queue
// If queue is running doesn't do anything
//
queue.run()
//
// This either runs or resumes the queue
// and adds the given closure to the lists of completions.
// You can add as many completions as you want (also half way)
// trough executing the queue.
//
queue.run { result in
print("====== completions ======")
print("initial completion: run")
}运行包含的演示应用程序,以查看上述示例中的一些示例动作。
授权
作者: Marin Todorov
许可
TaskQueue 在MIT许可下可用。详见LICENSE文件。