PYFMDB 0.0.5
- 作者
- pengyong
前言
之前一直做web开发,对于做web开发的人而言一定熟悉各种ORM,各种语言针对mysql的ORM有很多,比如PHP的各类框架yii、thinkphp、laravel,ruby语言的rails,GO语言的beego等。iOS开发则面对的数据库是sqlite。FMDB 是基于sqlite的数据库操作类,稳定,但用起来还是不够简洁,PYFMDB是基于FMDB的更高层次的数据库操作类。
程序介绍
PYFMDB分为三部分,PYFMDB基于FMDB负责数据库底层操作处理,PYTable是自定义Table的基类,提供基于具体数据库表的操作,是更高层次的封装PYFMDB,PYStructure是定义数据库表结构处理类。
快速入门
1.导入PYFMDB
您可以在Podfile中加入以下一行代码来使用PYFMDB:
pod 'PYFMDB'
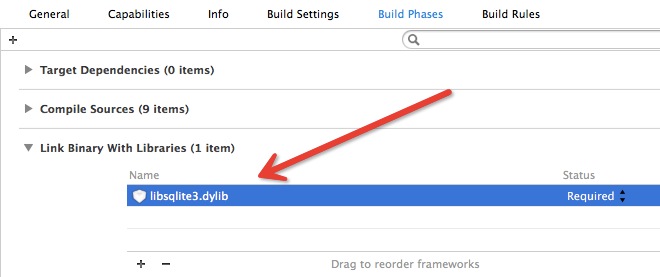
或者,您也可以手动添加源代码使用本项目,将开源代码中的PYFMDB和FMDB 目录添加到您的工程中,并在工程设置的“Link Binary With Libraries”中,增加libsqlite3.dylib,如下图所示:
2.创建自定义Table类
创建一个Table类继承PYTable,例如演示代码中创建了CarTable类。
设置数据库表名
在CarTable.m中重写如下方法
-(NSString *)tableName{
return @"car";
}
设置数据库表结构
在CarTable.m中重写如下方法
-(PYStructure *)structure{
PYStructure * st = [[PYStructure alloc] init];
[st addWithField:@"id" andType:PYStructureTypeAutoInc];
[st addWithField:@"name" andType:PYStructureTypeNormalText];
[st addWithField:@"wheels" andType:PYStructureTypeNormalInt];
return st;
}
PYStructureType是定义的结构体,PYStructureTypeAutoInc代表自增类型字段,PYStructureTypeNormalText代表普通文本字段,PYStructureTypeNormalInt代表普通int类型字段
3.自定义Table类的使用
table类可以实现针对当前table的增删改查数据库操作。
CarTable *table = [[CarTable alloc] init];
新增数据
NSDictionary *fields = @{@"name":@"宝马",@"wheels":@1};
[table addFields:fields];
删除数据
指定字段删除
NSString *where = @"name='宝马'";
[table deleteWithWhere:where];
多种条件删除
NSString *where = @"name='宝马' and id >=5";
[table deleteWithWhere:where];
清空数据表
[table truncate];
更新数据
更新多个字段
NSString *where = @"name='宝马'";
NSDictionary *fields = @{@"name":@"奔驰",@"wheels":@2};
[table updateFields:fields andWhere:where];
更新1个字段
[table setField:@"name" andValue:@"奔驰" andWhere:@"name='宝马'"];
查询数据
查询表全部数据,全部字段,返回的结果为NSArray
NSArray *results = [table selectAll];
按条件查询数据,全部字段,返回的结果为NSArray
NSString *where = @"name='宝马'";
NSArray *results = [table selectWithWhere:where];
按条件查询数据,指定字段,返回结果为NSArray 多个字段用半角逗号隔开
NSString *where = @"name='宝马'";
NSString *fields = @"id,wheels";
NSArray *results = [table selectWithWhere:where andFields:fields];
按条件查询数据,指定字段,设置分页,返回结果为NSArray 要查询全部字段时 用 * 代表查询全部字段
NSString *where = @"name='宝马'";
NSString *fields = @"id,wheels";
//NSString *fields = @"*";
NSArray *results = [table selectWithWhere:where andFields:fields andPage:1 andPageSize:10];//取第一页,每页10条
按条件查询数据,指定字段,设置分页,设置排序,返回结果为NSArray 排序中desc代表降序,asc代表升序 单个字段排序如id desc 多个字段排序如id,wheel asc
NSString *where = @"name='宝马'";
NSString *fields = @"id,wheels";
//NSString *fields = @"*";
NSArray *results = [table selectWithWhere:where andFields:fields andPage:1 andPageSize:10 andOrder:@"id desc"];
按条件查询单行数据,返回结果为NSDictionary
NSString *where = @"name='宝马'";
NSDictionary *result = [table findWithWhere:where];
按条件查询单行单个字段数据,返回结果为id类型
id result = [table getField:@"name" andWhere:@"id=1"];
统计表总行数
NSUInteger tableCount = [table count];
判断表是否为空
if([table isEmpty]){
//table is empty
}
调试信息
NSLog(@"dbpath:%@",table.databasePath);//数据库位置
NSLog(@"lastSql:%@",table.lastSql);//最后执行的sql
NSLog(@"dbname:%@",table.databaseName);//数据库名
NSLog(@"tablename:%@",table.tableName);//数据表名
NSLog(@"table structure:%@",table.structure.structureDictory);//数据表结构
NSLog(@"table fields:%@",table.structure.fieldsString);//数据表字段