Matft
Matft是一个类似于Numpy的Swift库。函数名称和用法与Numpy相似。
注意:您还可以使用协议版本(beta版本)。
特性 & 用法
-
许多类型
-
Pretty print
-
索引
- 积极
- 负
- 布尔
- 花哨
-
切片
- 开始 / 到 / 每
- 新轴
-
视图
- 赋值
-
转换
- 广播
- 转置
- 重塑
- .astype
-
通用函数减少
-
数学
- 算术
- 统计
- 线性代数
...等等。
有关所有函数的信息,请参阅函数列表。
声明
MfArray
-
MfArray类似于 numpy.ndarray
let a = MfArray([[[ -8, -7, -6, -5], [ -4, -3, -2, -1]], [[ 0, 1, 2, 3], [ 4, 5, 6, 7]]]) let aa = Matft.arange(start: -8, to: 8, by: 1, shape: [2,2,4]) print(a) print(aa) /* mfarray = [[[ -8, -7, -6, -5], [ -4, -3, -2, -1]], [[ 0, 1, 2, 3], [ 4, 5, 6, 7]]], type=Int, shape=[2, 2, 4] mfarray = [[[ -8, -7, -6, -5], [ -4, -3, -2, -1]], [[ 0, 1, 2, 3], [ 4, 5, 6, 7]]], type=Int, shape=[2, 2, 4] */
MfType
-
您可以将
MfType作为MfArray的参数 mftype: .Hoge传入。它与dtype相似。※注意,即使设置了MfType.Int,存储的数据类型也仅限于Float或Double。因此,如果您向MfArray输入大数字,可能会在加减乘除等任何计算中导致溢出或产生奇怪的结果。但是,我相信这在实际应用中不会成为问题。
-
MfType列表如下
public enum MfType: Int{ case None // Unsupportted case Bool case UInt8 case UInt16 case UInt32 case UInt64 case UInt case Int8 case Int16 case Int32 case Int64 case Int case Float case Double case Object // Unsupported }
-
此外,您还可以使用
astype轻松地将MfType转换为其他类型let a = MfArray([[[ -8, -7, -6, -5], [ -4, -3, -2, -1]], [[ 0, 1, 2, 3], [ 4, 5, 6, 7]]]) print(a)//See above. if mftype is not passed, MfArray infer MfType. In this example, it's MfType.Int let a = MfArray([[[ -8, -7, -6, -5], [ -4, -3, -2, -1]], [[ 0, 1, 2, 3], [ 4, 5, 6, 7]]], mftype: .Float) print(a) /* mfarray = [[[ -8.0, -7.0, -6.0, -5.0], [ -4.0, -3.0, -2.0, -1.0]], [[ 0.0, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0], [ 4.0, 5.0, 6.0, 7.0]]], type=Float, shape=[2, 2, 4] */ let aa = MfArray([[[ -8, -7, -6, -5], [ -4, -3, -2, -1]], [[ 0, 1, 2, 3], [ 4, 5, 6, 7]]], mftype: .UInt) print(aa) /* mfarray = [[[ 4294967288, 4294967289, 4294967290, 4294967291], [ 4294967292, 4294967293, 4294967294, 4294967295]], [[ 0, 1, 2, 3], [ 4, 5, 6, 7]]], type=UInt, shape=[2, 2, 4] */ //Above output is same as numpy! /* >>> np.arange(-8, 8, dtype=np.uint32).reshape(2,2,4) array([[[4294967288, 4294967289, 4294967290, 4294967291], [4294967292, 4294967293, 4294967294, 4294967295]], [[ 0, 1, 2, 3], [ 4, 5, 6, 7]]], dtype=uint32) */ print(aa.astype(.Float)) /* mfarray = [[[ -8.0, -7.0, -6.0, -5.0], [ -4.0, -3.0, -2.0, -1.0]], [[ 0.0, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0], [ 4.0, 5.0, 6.0, 7.0]]], type=Float, shape=[2, 2, 4] */
Subscription
MfSlice
- 您可以使用下标访问特定数据。
您可以将以下列表中的MfSlice设置为下标。
-
MfSlice(start: Int? = nil, to: Int? = nil, by: Int = 1)
-
Matft.newaxis -
~< //this is prefix, postfix and infix operator. same as python's slice, ":"
(正向) 索引
-
常规索引
let a = Matft.arange(start: 0, to: 27, by: 1, shape: [3,3,3]) print(a) /* mfarray = [[[ 0, 1, 2], [ 3, 4, 5], [ 6, 7, 8]], [[ 9, 10, 11], [ 12, 13, 14], [ 15, 16, 17]], [[ 18, 19, 20], [ 21, 22, 23], [ 24, 25, 26]]], type=Int, shape=[3, 3, 3] */ print(a[2,1,0]) // 21
切片
-
如果您将
:替换为~<,就可以得到切片后的mfarray。注意使用a[0~<]而不是a[:]来获取轴上的所有元素。print(a[~<1]) //same as a[:1] for numpy /* mfarray = [[[ 9, 10, 11], [ 12, 13, 14], [ 15, 16, 17]]], type=Int, shape=[1, 3, 3] */ print(a[1~<3]) //same as a[1:3] for numpy /* mfarray = [[[ 9, 10, 11], [ 12, 13, 14], [ 15, 16, 17]], [[ 18, 19, 20], [ 21, 22, 23], [ 24, 25, 26]]], type=Int, shape=[2, 3, 3] */ print(a[~<~<2]) //same as a[::2] for numpy //print(a[~<<2]) //alias /* mfarray = [[[ 0, 1, 2], [ 3, 4, 5], [ 6, 7, 8]], [[ 18, 19, 20], [ 21, 22, 23], [ 24, 25, 26]]], type=Int, shape=[2, 3, 3] */
负索引
-
负索引也是可用的...这对我来说是最难实现的...
print(a[~<-1]) /* mfarray = [[[ 0, 1, 2], [ 3, 4, 5], [ 6, 7, 8]], [[ 9, 10, 11], [ 12, 13, 14], [ 15, 16, 17]]], type=Int, shape=[2, 3, 3] */ print(a[-1~<-3]) /* mfarray = [], type=Int, shape=[0, 3, 3] */ print(a[~<~<-1]) //print(a[~<<-1]) //alias /* mfarray = [[[ 18, 19, 20], [ 21, 22, 23], [ 24, 25, 26]], [[ 9, 10, 11], [ 12, 13, 14], [ 15, 16, 17]], [[ 0, 1, 2], [ 3, 4, 5], [ 6, 7, 8]]], type=Int, shape=[3, 3, 3]*/
布尔索引
-
您可以使用布尔索引。
请注意!我没有检查性能,因此这种布尔索引可能很慢。不幸的是,Matft 比 numpy 慢得多...
(numpy 需要 1ms,Matft 需要 7ms...)
let img = MfArray([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]], mftype: .UInt8) img[img > 3] = MfArray([10], mftype: .UInt8) print(img) /* mfarray = [[ 1, 2, 3], [ 10, 10, 10], [ 10, 10, 10]], type=UInt8, shape=[3, 3] */
花式索引
-
您可以使用花式索引!!!
let a = MfArray([[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]]) a[MfArray([0, 1, 2]), MfArray([0, -1, 0])] = MfArray([999,888,777]) print(a) /* mfarray = [[ 999, 2], [ 3, 888], [ 777, 6]], type=Int, shape=[3, 2] */ a.T[MfArray([0, 1, -1]), MfArray([0, 1, 0])] = MfArray([-999,-888,-777]) print(a) /* mfarray = [[ -999, -777], [ 3, -888], [ 777, 6]], type=Int, shape=[3, 2] */
视图
-
注意,返回的切片mfarray将有
base属性(类似于Numpy中的view)。请详细查看numpy文档。let a = Matft.arange(start: 0, to: 4*4*2, by: 1, shape: [4,4,2]) let b = a[0~<, 1] b[~<<-1] = MfArray([9999]) // cannot pass Int directly such like 9999 print(a) /* mfarray = [[[ 0, 1], [ 9999, 9999], [ 4, 5], [ 6, 7]], [[ 8, 9], [ 9999, 9999], [ 12, 13], [ 14, 15]], [[ 16, 17], [ 9999, 9999], [ 20, 21], [ 22, 23]], [[ 24, 25], [ 9999, 9999], [ 28, 29], [ 30, 31]]], type=Int, shape=[4, 4, 2] */
函数列表
以下是最全的Matft函数列表。如上所述,几乎所有功能都与Numpy相似。此外,这些函数在内部使用Accelerate框架,性能可能保持很高。
*表示.method存在。简而言之,您可以在a.shallowcopy()中使用a作为MfArray。
^表示只有.method。简而言之,您可以使用a.tolist()而不是Matft.tolist,其中a是MfArray。
- 创建
| Matft | Numpy |
|---|---|
| *Matft.shallowcopy | *numpy.copy |
| *Matft.deepcopy | copy.deepcopy |
| Matft.nums | numpy.ones * N |
| Matft.nums_like | numpy.ones_like * N |
| Matft.arange | numpy.arange |
| Matft.eye | numpy.eye |
| Matft.diag | numpy.diag |
| Matft.vstack | numpy.vstack |
| Matft.hstack | numpy.hstack |
| Matft.concatenate | numpy.concatenate |
| Matft.append | numpy.append |
| Matft.insert | numpy.insert |
| Matft.take | numpy.take |
- 转换
| Matft | Numpy |
|---|---|
| Matft.astype | numpy.astype |
| Matft.transpose | numpy.transpose |
| Matft.expand_dims | numpy.expand_dims |
| Matft.squeeze | numpy.squeeze |
| Matft.broadcast_to | numpy.broadcast_to |
| Matft.conv_order | numpy.ascontiguousarray |
| Matft.flatten | numpy.flatten |
| Matft.flip | numpy.flip |
| Matft.clip | numpy.clip |
| Matft.swapaxes | numpy.swapaxes |
| Matft.moveaxis | numpy.moveaxis |
| Matft.sort | numpy.sort |
| Matft.argsort | numpy.argsort |
| MfArray.toArray | numpy.ndarray.tolist |
-
文件
保存函数尚未开发。
| Matft | Numpy |
|---|---|
| Matft.file.loadtxt | numpy.loadtxt |
| Matft.file.genfromtxt | numpy.genfromtxt |
-
操作
第 2 行是中缀(前缀)操作符。
| Matft | Numpy |
|---|---|
| Matft.add + |
numpy.add + |
| Matft.sub - |
numpy.sub - |
| Matft.div / |
numpy.div . |
| Matft.mul * |
numpy.multiply * |
| Matft.inner *+ |
numpy.inner 无 |
| Matft.cross *^ |
numpy.cross 无 |
| Matft.matmul & |
numpy.matmul @ |
| Matft.equal === |
numpy.equal == |
| Matft.not_equal !== |
numpy.not_equal != |
| Matft.less < |
numpy.less < |
| Matft.less_equal <= |
numpy.less_equal <= |
| Matft.greater > |
numpy.greater > |
| Matft.greater_equal >= |
numpy.greater_equal >= |
| Matft.allEqual == |
numpy.array_equal 无 |
| Matft.neg - |
numpy.negative - |
- 通用函数归约
| Matft | Numpy |
|---|---|
| Matft.ufuncReduce 例如) Matft.ufuncReduce(a, Matft.add) |
numpy.add.reduce 例如) numpy.add.reduce(a) |
| Matft.ufuncAccumulate 例如) Matft.ufuncAccumulate(a, Matft.add) |
numpy.add.accumulate 例如) numpy.add.accumulate(a) |
- 数学函数
| Matft | Numpy |
|---|---|
| Matft.math.sin | numpy.sin |
| Matft.math.asin | numpy.asin |
| Matft.math.sinh | numpy.sinh |
| Matft.math.asinh | numpy.asinh |
| Matft.math.sin | numpy.cos |
| Matft.math.acos | numpy.acos |
| Matft.math.cosh | numpy.cosh |
| Matft.math.acosh | numpy.acosh |
| Matft.math.tan | numpy.tan |
| Matft.math.atan | numpy.atan |
| Matft.math.tanh | numpy.tanh |
| Matft.math.atanh | numpy.atanh |
| Matft.math.sqrt | numpy.sqrt |
| Matft.math.rsqrt | numpy.rsqrt |
| Matft.math.exp | numpy.exp |
| Matft.math.log | numpy.log |
| Matft.math.log2 | numpy.log2 |
| Matft.math.log10 | numpy.log10 |
| Matft.math.ceil | numpy.ceil |
| Matft.math.floor | numpy.floor |
| Matft.math.trunc | numpy.trunc |
| Matft.math.nearest | numpy.nearest |
| Matft.math.round | numpy.round |
| Matft.math.abs | numpy.abs |
| Matft.math.reciprocal | numpy.reciprocal |
| Matft.math.power | numpy.power |
| Matft.math.square | numpy.square |
| Matft.math.sign | numpy.sign |
- 统计函数
| Matft | Numpy |
|---|---|
| Matft.stats.mean | numpy.mean |
| Matft.stats.max | numpy.max |
| Matft.stats.argmax | numpy.argmax |
| Matft.stats.min | numpy.min |
| Matft.stats.argmin | numpy.argmin |
| Matft.stats.sum | numpy.sum |
| Matft.stats.maximum | numpy.maximum |
| Matft.stats.minimum | numpy.minimum |
| Matft.stats.sumsqrt | 无 |
| Matft.stats.squaresum | 无 |
| Matft.stats.cumsum | numpy.cumsum |
- 线性代数
| Matft | Numpy |
|---|---|
| Matft.linalg.solve | numpy.linalg.solve |
| Matft.linalg.inv | numpy.linalg.inv |
| Matft.linalg.det | numpy.linalg.det |
| Matft.linalg.eigen | numpy.linalg.eig |
| Matft.linalg.svd | numpy.linalg.svd |
| Matft.linalg.pinv | numpy.linalg.pinv |
| Matft.linalg.polar_left | scipy.linalg.polar |
| Matft.linalg.polar_right | scipy.linalg.polar |
| Matft.linalg.normlp_vec | scipy.linalg.norm |
| Matft.linalg.normfro_mat | scipy.linalg.norm |
| Matft.linalg.normnuc_mat | scipy.linalg.norm |
- 插值
Matft只支持自然三次样条。我将在以后实现其他边界条件。
| Matft | Numpy |
|---|---|
| Matft.interp1d.cubicSpline | scipy.interpolation.CubicSpline |
性能
我使用了Accelerate,所以MfArray的所有操作都可能保持高性能。
func testPefAdd1() {
do{
let a = Matft.arange(start: 0, to: 10*10*10*10*10*10, by: 1, shape: [10,10,10,10,10,10])
let b = Matft.arange(start: 0, to: -10*10*10*10*10*10, by: -1, shape: [10,10,10,10,10,10])
self.measure {
let _ = a+b
}
/*
'-[MatftTests.ArithmeticPefTests testPefAdd1]' measured [Time, seconds] average: 0.001, relative standard deviation: 23.418%, values: [0.001707, 0.001141, 0.000999, 0.000969, 0.001029, 0.000979, 0.001031, 0.000986, 0.000963, 0.001631]
1.14ms
*/
}
}
func testPefAdd2(){
do{
let a = Matft.arange(start: 0, to: 10*10*10*10*10*10, by: 1, shape: [10,10,10,10,10,10])
let b = a.transpose(axes: [0,3,4,2,1,5])
let c = a.T
self.measure {
let _ = b+c
}
/*
'-[MatftTests.ArithmeticPefTests testPefAdd2]' measured [Time, seconds] average: 0.004, relative standard deviation: 5.842%, values: [0.004680, 0.003993, 0.004159, 0.004564, 0.003955, 0.004200, 0.003998, 0.004317, 0.003919, 0.004248]
4.20ms
*/
}
}
func testPefAdd3(){
do{
let a = Matft.arange(start: 0, to: 10*10*10*10*10*10, by: 1, shape: [10,10,10,10,10,10])
let b = a.transpose(axes: [1,2,3,4,5,0])
let c = a.T
self.measure {
let _ = b+c
}
/*
'-[MatftTests.ArithmeticPefTests testPefAdd3]' measured [Time, seconds] average: 0.004, relative standard deviation: 16.815%, values: [0.004906, 0.003785, 0.003702, 0.005981, 0.004261, 0.003665, 0.004083, 0.003654, 0.003836, 0.003874]
4.17ms
*/
}Matft的性能几乎与Numpy相同!!
※Swift的性能测试是在发布模式下进行的
我的代码有几个开销和冗余部分,所以这个性能可能比现在更好。
import numpy as np
#import timeit
a = np.arange(10**6).reshape((10,10,10,10,10,10))
b = np.arange(0, -10**6, -1).reshape((10,10,10,10,10,10))
#timeit.timeit("b+c", repeat=10, globals=globals())
%timeit -n 10 a+b
"""
962 µs ± 273 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10 loops each)
"""
a = np.arange(10**6).reshape((10,10,10,10,10,10))
b = a.transpose((0,3,4,2,1,5))
c = a.T
#timeit.timeit("b+c", repeat=10, globals=globals())
%timeit -n 10 b+c
"""
5.68 ms ± 1.45 ms per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10 loops each)
"""
a = np.arange(10**6).reshape((10,10,10,10,10,10))
b = a.transpose((1,2,3,4,5,0))
c = a.T
#timeit.timeit("b+c", repeat=10, globals=globals())
%timeit -n 10 b+c
"""
3.92 ms ± 897 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10 loops each)
"""安装
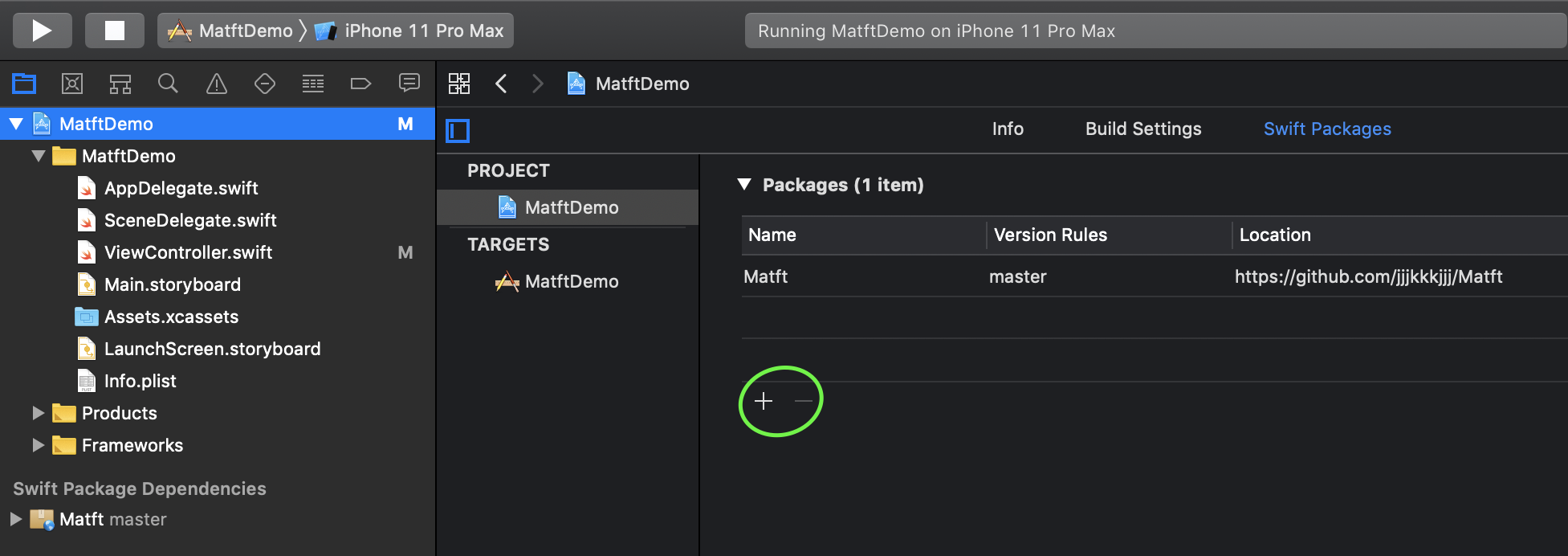
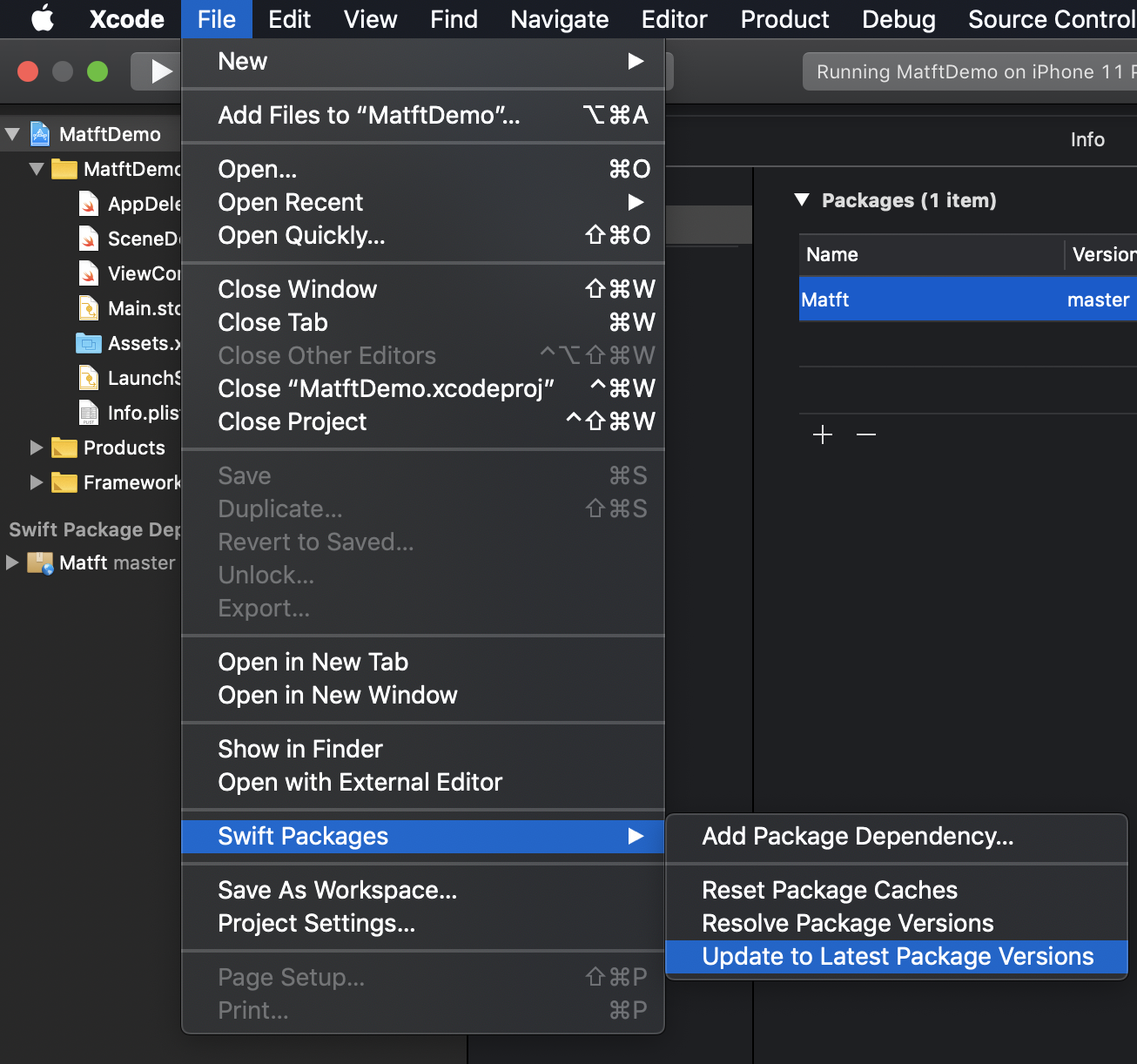
SwiftPM
Carthage
-
设置Cartfile
echo 'github "jjjkkkjjj/Matft"' > Cartfile carthage update ###or append '--platform ios' -
将上述步骤生成的Matft.framework导入到您的项目中
CocoaPods
-
创建Podfile (如果已经创建,请跳过)
pod init
-
在Podfile中写入如下所示的
pod 'Matft'target 'your project' do pod 'Matft' end
-
安装Matft
pod install