FastEasyMapping 1.2.2
| 测试已测试 | ✗ |
| Lang语言 | Obj-CObjective C |
| 许可证 | MIT |
| 发布最新发布 | 2017年6月 |
由Dima Shemet,Dima Zen,name=Dima Vorona维护。
FastEasyMapping 1.2.2
- 由
- Dima Zen
注意
这是 EasyMapping 的衍生,一个灵活且简单的 JSON 映射框架。
概述
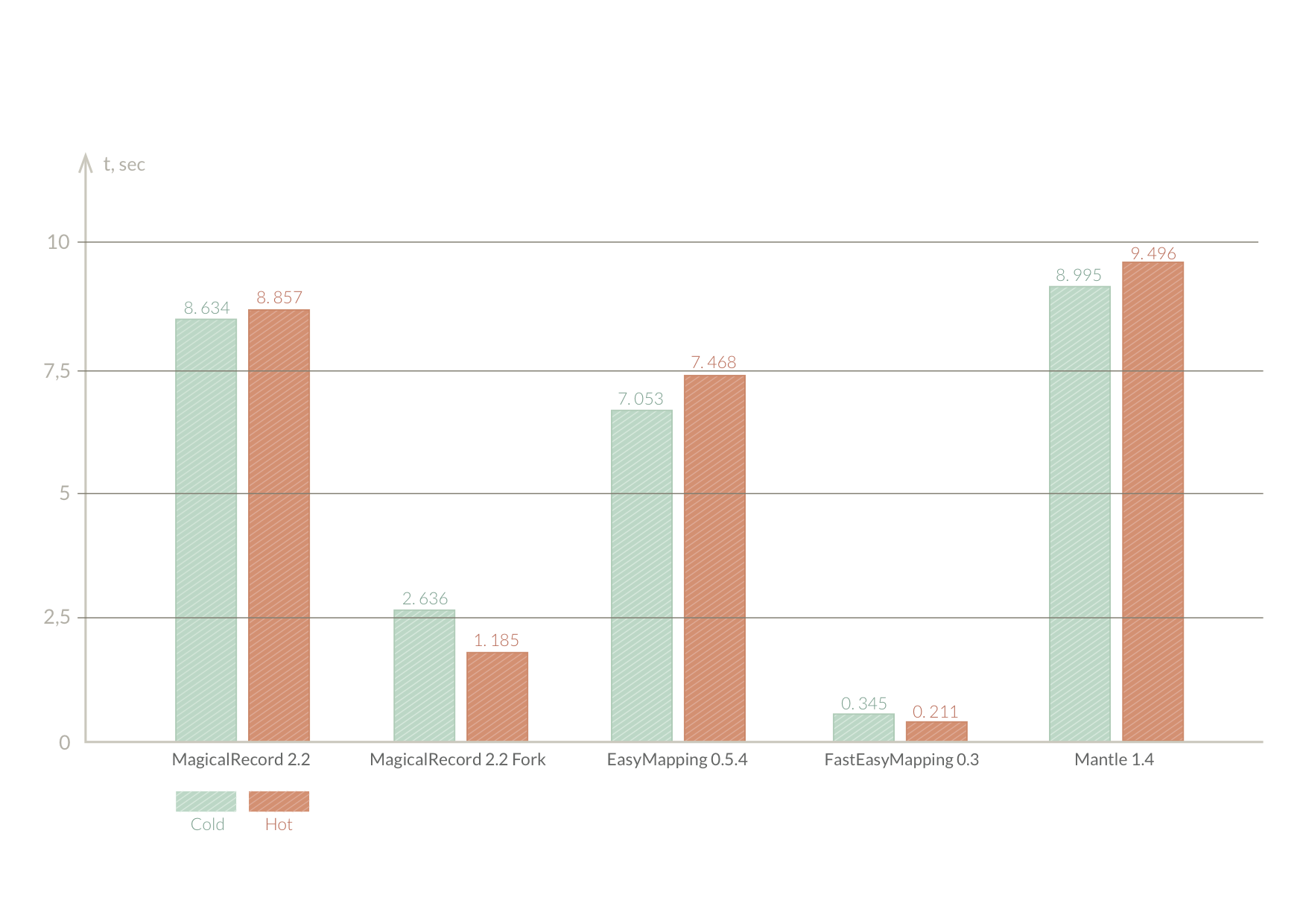
我们发现,几乎所有流行的 JSON 映射库都相当慢。主要原因是在查找现有对象时需要多次访问数据库。我们决定提升现有解决方案(即 EasyMapping)的整体性能。
2014年6月进行的基准测试。结果可能已过时(EasyMapping 的性能几乎相同)。
要求
| 平台 | 最低部署目标 |
|---|---|
| iOS | 8.0 |
| macOS | 10.10 |
| tvOS | 9.0 |
| watchOS | 2.0 |
使用 Xcode 8.3.2+ 构建
使用
反序列化
今天支持 NSObject 和 NSManagedObject 的映射。让我们看看基本映射是如何实现的:例如,我们有一个 JSON
{
"name": "Lucas",
"user_email": "[email protected]",
"car": {
"model": "i30",
"year": "2013"
},
"phones": [
{
"ddi": "55",
"ddd": "85",
"number": "1111-1111"
},
{
"ddi": "55",
"ddd": "11",
"number": "2222-222"
}
]
}以及相应的由 CoreData 生成的类
@interface Person : NSManagedObject
@property (nonatomic, retain) NSString *name;
@property (nonatomic, retain) NSString *email;
@property (nonatomic, retain) Car *car;
@property (nonatomic, retain) NSSet *phones;
@end
@interface Car : NSManagedObject
@property (nonatomic, retain) NSString *model;
@property (nonatomic, retain) NSString *year;
@property (nonatomic, retain) Person *person;
@end
@interface Phone : NSManagedObject
@property (nonatomic, retain) NSString *ddi;
@property (nonatomic, retain) NSString *ddd;
@property (nonatomic, retain) NSString *number;
@property (nonatomic, retain) Person *person;
@end为了映射 JSON 到对象 和相反,我们必须描述映射规则
@implementation Person (Mapping)
+ (FEMMapping *)defaultMapping {
FEMMapping *mapping = [[FEMMapping alloc] initWithEntityName:@"Person"];
[mapping addAttributesFromArray:@[@"name"]];
[mapping addAttributesFromDictionary:@{@"email": @"user_email"}];
[mapping addRelationshipMapping:[Car defaultMapping] forProperty:@"car" keyPath:@"car"];
[mapping addToManyRelationshipMapping:[Phone defaultMapping] forProperty:@"phones" keyPath:@"phones"];
return mapping;
}
@end
@implementation Car (Mapping)
+ (FEMMapping *)defaultMapping {
FEMMapping *mapping = [[FEMMapping alloc] initWithEntityName:@"Car"];
[mapping addAttributesFromArray:@[@"model", @"year"]];
return mapping;
}
@end
@implementation Phone (Mapping)
+ (FEMMapping *)defaultMapping {
FEMMapping *mapping = [[FEMMapping alloc] initWithEntityName:@"Phone"];
[mapping addAttributesFromArray:@[@"number", @"ddd", @"ddi"]];
return mapping;
}
@end现在我们可以轻松地将 JSON 反序列化为对象
FEMMapping *mapping = [Person defaultMapping];
Person *person = [FEMDeserializer objectFromRepresentation:json mapping:mapping context:managedObjectContext];或对象的集合
NSArray *persons = [FEMDeserializer collectionFromRepresentation:json mapping:mapping context:managedObjectContext];或者更新一个对象
[FEMDeserializer fillObject:person fromRepresentation:json mapping:mapping];
序列化
我们还可以使用上面定义的映射将 对象序列化为 JSON
FEMMapping *mapping = [Person defaultMapping];
Person *person = ...;
NSDictionary *json = [FEMSerializer serializeObject:person usingMapping:mapping];或集合序列化为 JSON
FEMMapping *mapping = [Person defaultMapping];
NSArray *persons = ...;
NSArray *json = [FEMSerializer serializeCollection:persons usingMapping:mapping];映射
FEMAttribute
FEMAttribute 是 FEM 的核心类。简单来说,它是描述对象 属性 和 JSON 的 keyPath 之间关系的描述。它还封装了将值从 对象映射到 JSON 及其返回的块的知识。
typedef __nullable id (^FEMMapBlock)(id value __nonnull);
@interface FEMAttribute : NSObject <FEMProperty>
@property (nonatomic, copy, nonnull) NSString *property;
@property (nonatomic, copy, nullable) NSString *keyPath;
- (nonnull instancetype)initWithProperty:(nonnull NSString *)property keyPath:(nullable NSString *)keyPath map:(nullable FEMMapBlock)map reverseMap:(nullable FEMMapBlock)reverseMap;
- (nullable id)mapValue:(nullable id)value;
- (nullable id)reverseMapValue:(nullable id)value;
@end除了property和keyPath值之外,您还可以传递映射块,允许您描述完全定制的映射。
示例
具有相同键和类型的值映射
FEMAttribute *attribute = [FEMAttribute mappingOfProperty:@"url"];
// or
FEMAttribute *attribute = [[FEMAttribute alloc] initWithProperty:@"url" keyPath:@"url" map:NULL reverseMap:NULL];具有不同键和相同类型的值映射
FEMAttribute *attribute = [FEMAttribute mappingOfProperty:@"urlString" toKeyPath:@"URL"];
// or
FEMAttribute *attribute = [[FEMAttribute alloc] initWithProperty:@"urlString" keyPath:@"URL" map:NULL reverseMap:NULL];不同类型的映射
在JSON中,值类型经常需要转换为更有用的内部表示。例如,将十六进制转换为UIColor,将String转换为NSURL,将Integer转换为enum等等。为此,您可以使用map和reverseMap属性。例如,让我们描述一个属性,它使用NSDate和NSDateFormatter将String映射为NSDate。
NSDateFormatter *formatter = [[NSDateFormatter alloc] init];
[formatter setLocale:[[NSLocale alloc] initWithLocaleIdentifier:@"en_US_POSIX"]];
[formatter setTimeZone:[NSTimeZone timeZoneWithAbbreviation:@"UTC"]];
[formatter setDateFormat:@"yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss.SSS'Z'"];
FEMAttribute *attribute = [[FEMAttribute alloc] initWithProperty:@"updateDate" keyPath:@"timestamp" map:^id(id value) {
if ([value isKindOfClass:[NSString class]]) {
return [formatter dateFromString:value];
}
return nil;
} reverseMap:^id(id value) {
return [formatter stringFromDate:value];
}];首先,我们定义了满足我们要求的NSDateFormatter。下一步是定义具有正确映射的属性实例。简而言之,map块在反序列化(JSON到对象)过程中调用,而reverseMap用于序列化过程。这两个块都很简单,但也有一些陷阱。
-
map可以接收NSNull实例。这在JSON中对应于空值。 - 对于缺少的键,
map不会调用。因此,如果JSON不包含您的属性指定的键路径,则不调用反向映射。 - 从
map返回nil或NSNull以处理空值 -
仅当
property包含非空值时才调用reverseMap。 - 从
reverseMap返回nil或NSNull。这两者都将产生{"keyPath": null}
向FEMMapping添加属性
有几个快捷方式可以更容易地将属性添加到映射本身。
显式添加
FEMMapping *mapping = [[FEMMapping alloc] initWithObjectClass:[Person class]];
FEMAttribute *attribute = [FEMAttribute mappingOfProperty:@"url"];
[mapping addAttribute:attribute];隐式添加
FEMMapping *mapping = [[FEMMapping alloc] initWithObjectClass:[Person class]];
[mapping addAttributeWithProperty:@"property" keyPath:@"keyPath"];作为字典添加
FEMMapping *mapping = [[FEMMapping alloc] initWithObjectClass:[Person class]];
[mapping addAttributesFromDictionary:@{@"property": @"keyPath"}];作为数组添加
当property等于keyPath时非常有用
FEMMapping *mapping = [[FEMMapping alloc] initWithObjectClass:[Person class]];
[mapping addAttributesFromArray:@[@"propertyAndKeyPathAreTheSame"]];FEMRelationship
FEMRelationship是一个类,描述了两个FEMMapping实例之间的关系。
@interface FEMRelationship
@property (nonatomic, copy, nonnull) NSString *property;
@property (nonatomic, copy, nullable) NSString *keyPath;
@property (nonatomic, strong, nonnull) FEMMapping *mapping;
@property (nonatomic, getter=isToMany) BOOL toMany;
@property (nonatomic) BOOL weak;
@property (nonatomic, copy, nonnull) FEMAssignmentPolicy assignmentPolicy;
@end该关系也与一个property和一个keyPath相关联。显然,它引用了对象的FEMMapping,还有一个表示是否是多对一关系的标志。此外,它允许您指定关系赋值策略和“语义化”行为。
示例
FEMMapping *childMapping = ...;
FEMRelationship *childRelationship = [[FEMRelationship alloc] initWithProperty:@"parentProperty" keyPath:@"jsonKeyPath" mapping:childMapping];
childRelationship.toMany = YES;赋值策略
赋值策略描述了如何将反序列化的关系值分配给属性。FEM支持5种内置策略。
-
FEMAssignmentPolicyAssign- 用新值替换旧的属性值。适用于一对一和多对一关系。默认策略。 -
FEMAssignmentPolicyObjectMerge- 如果不是nil,则分配新的关系值。适用于一对一关系。 -
FEMAssignmentPolicyCollectionMerge- 合并关系的新旧值。支持的集合有:NSSet、NSArray、NSOrderedSet 及其后续者。适用于一对多关系。 -
FEMAssignmentPolicyObjectReplace- 通过删除旧值来替换旧值为新值。适用于一对一关系。 -
FEMAssignmentPolicyCollectionReplace- 删除新旧值集合的并集中不存在的对象。并集集合作为新值使用。支持的集合有:NSSet、NSArray、NSOrderedSet 及其后续者。适用于一对多关系。
将关系添加到 FEMMapping
显式地
FEMMapping *mapping = [[FEMMapping alloc] initWithObjectClass:[Person class]];
FEMMapping *carMapping = [[FEMMapping alloc] initWithObjectClass:[Car class]];
FEMRelationship *carRelationship = [[FEMRelationship alloc] initWithProperty:@"car" keyPath:@"car" mapping:carMapping];
[mapping addRelationship:carRelationship];隐式地
FEMMapping *mapping = [[FEMMapping alloc] initWithObjectClass:[Person class]];
FEMMapping *phoneMapping = [[FEMMapping alloc] initWithObjectClass:[Phone class]];
[mapping addToManyRelationshipMapping:phoneMapping property:@"phones" keyPath:@"phones"];FEMMapping
通常,FEMMapping 是一个类,通过封装一组属性和关系描述了对 NSObject 或 NSManagedObject 的映射。此外,它还定义了对象唯一性的可能性(仅由 CoreData 支持)。
NSObject 和 NSManagedObject 之间的唯一区别在于它们的 init 方法。
NSObject
FEMMapping *objectMapping = [[FEMMapping alloc] initWithObjectClass:[CustomNSObjectSuccessor class]];NSManagedObject
FEMMapping *managedObjectMapping = [[FEMMapping alloc] initWithEntityName:@"EntityName"];根路径
有时所需的 JSON 是通过键路径嵌套的。在这种情况下,您可以使用 rootPath 属性。让我们通过嵌套 Person 表示来修改 Person JSON
{
result: {
"name": "Lucas",
"user_email": "[email protected]",
"car": {
"model": "i30",
"year": "2013"
}
}
}
映射将看起来像这样
@implementation Person (Mapping)
+ (FEMMapping *)defaultMapping {
FEMMapping *mapping = [[FEMMapping alloc] initWithEntityName:@"Person"];
mapping.rootPath = @"result";
[mapping addAttributesFromArray:@[@"name"]];
[mapping addAttributesFromDictionary:@{@"email": @"user_email"}];
[mapping addRelationshipMapping:[Car defaultMapping] forProperty:@"car" keyPath:@"car"];
return mapping;
}
@end重要提示:在关系映射期间忽略
FEMMapping.rootPath。请使用FEMRelationship.keyPath代替!
唯一性
当你将 JSON 反序列化为 CoreData 且不希望在数据库中重复数据时,这是一个常见的情况。这可以通过利用 FEMMapping.primaryKey 来轻松实现。它告知 FEMDeserializer 跟踪主键并避免数据复制。例如,让我们将 Person 的 email 设置为主键属性
@implementation Person (Mapping)
+ (FEMMapping *)defaultMapping {
FEMMapping *mapping = [[FEMMapping alloc] initWithEntityName:@"Person"];
mapping.primaryKey = @"email";
[mapping addAttributesFromArray:@[@"name"]];
[mapping addAttributesFromDictionary:@{@"email": @"user_email"}];
[mapping addRelationshipMapping:[Car defaultMapping] forProperty:@"car" keyPath:@"car"];
return mapping;
}
@end我们建议在 datamodel 中为主键建立索引,以加快键查找速度。主键支持的值是字符串和整数。
从第二次导入开始,FEMDeserializer 将更新现有的 Person。
通过 PK 绑定关系
有时对象表示包含由目标实体 PK 描述的关系
{
"result": {
"id": 314
"title": "https://github.com"
"category": 4
}
}
如您所见,从 JSON 中有两个对象:Website 和 Category。如果 Website 可以轻松导入,则存在对 Category 的外部引用,该引用由其主键 id 表示。我们能否将 Website 绑定到相应的类别?当然可以!我们只需将 Website 的表示法作为 Category 处理即可
首先,让我们声明我们的类
@interface Website: NSManagedObject
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSNumber *identifier;
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSString *title;
@property (nonatomic, strong) Category *category;
@end
@interface Category: NSManagedObject
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSNumber *identifier;
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSString *title;
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSSet *websites
@end现在定义 Website 的映射的时间到了
@implementation Website (Mapping)
+ (FEMMapping *)defaultMapping {
FEMMapping *mapping = [[FEMMapping alloc] initWithEntityName:@"Website"];
mapping.primaryKey = @"identifier";
[mapping addAttributesFromDictionary:@{@"identifier": @"id", @"title": @"title"}];
FEMMapping *categoryMapping = [[FEMMapping alloc] initWithEntityName:@"Category"];
categoryMapping.primaryKey = @"identifier";
[categoryMapping addAttributesFromDictionary:@{@"identifier": @"category"}];
[mapping addRelationshipMapping:categoryMapping property:@"category" keyPath:nil];
return mapping;
}
@end
指定nil作为Website类别表示的keyPath,它会被视为同等的Category。这样很容易绑定通过PK(这在网络中非常常见)传递的对象。
弱关系
在上面的例子中存在一个问题:如果我们的数据库中没有具有PK = 4的Category,怎么办?默认情况下,FEMDeserializer在反序列化的过程中会懒地创建新对象。在我们的情况下,这会导致插入没有任何数据除了identifier的Category实例。为了防止这种不一致,我们可以将FEMRelationship.weak设置为YES
@implementation Website (Mapping)
+ (FEMMapping *)defaultMapping {
FEMMapping *mapping = [[FEMMapping alloc] initWithEntityName:@"Website"];
mapping.primaryKey = @"identifier";
[mapping addAttributesFromDictionary:@{@"identifier": @"id", @"title": @"title"}];
FEMMapping *categoryMapping = [[FEMMapping alloc] initWithEntityName:@"Category"];
categoryMapping.primaryKey = @"identifier";
[categoryMapping addAttributeWithProperty:@"identifier" keyPath:nil];
FEMRelationship *categoryRelationship = [[FEMRelationship alloc] initWithProperty:@"category" keyPath:@"category" mapping:categoryMapping];
categoryRelationship.weak = YES;
[mapping addRelationship:categoryRelationship];
return mapping;
}
@end
结果是将Website与相应的Category绑定,仅当后者存在时。
委派
您可以通过实现FEMDeserializerDelegate协议来自定义反序列化过程
@protocol FEMDeserializerDelegate <NSObject>
@optional
- (void)deserializer:(nonnull FEMDeserializer *)deserializer willMapObjectFromRepresentation:(nonnull id)representation mapping:(nonnull FEMMapping *)mapping;
- (void)deserializer:(nonnull FEMDeserializer *)deserializer didMapObject:(nonnull id)object fromRepresentation:(nonnull id)representation mapping:(nonnull FEMMapping *)mapping;
- (void)deserializer:(nonnull FEMDeserializer *)deserializer willMapCollectionFromRepresentation:(nonnull NSArray *)representation mapping:(nonnull FEMMapping *)mapping;
- (void)deserializer:(nonnull FEMDeserializer *)deserializer didMapCollection:(nonnull NSArray *)collection fromRepresentation:(nonnull NSArray *)representation mapping:(nonnull FEMMapping *)mapping;
@end然而,如果您使用委派,您还必须手动实例化FEMDeserializer
NSObject
FEMDeserializer *deserializer = [[FEMDeserializer alloc] init];
deserializer.delegate = self;NSManagedObject
FEMDeserializer *deserializer = [[FEMDeserializer alloc] initWithContext:managedObjectContext];
deserializer.delegate = self;注意,在反序列化期间,将对每个对象和集合调用委派方法。让我们用Person的例子来说明
{
"name": "Lucas",
"user_email": "[email protected]",
"phones": [
{
"ddi": "55",
"ddd": "85",
"number": "1111-1111"
}
]
}
映射
@implementation Person (Mapping)
+ (FEMMapping *)defaultMapping {
FEMMapping *mapping = [[FEMMapping alloc] initWithEntityName:@"Person"];
[mapping addAttributesFromArray:@[@"name"]];
[mapping addAttributesFromDictionary:@{@"email": @"user_email"}];
[mapping addToManyRelationshipMapping:[Person defaultMapping] forProperty:@"phones" keyPath:@"phones"];
return mapping;
}
@end
@implementation Phone (Mapping)
+ (FEMMapping *)defaultMapping {
FEMMapping *mapping = [[FEMMapping alloc] initWithEntityName:@"Phone"];
[mapping addAttributesFromArray:@[@"number", @"ddd", @"ddi"]];
return mapping;
}
@end在人员的集合反序列化过程中,将按以下顺序执行
- willMapCollectionFromRepresentation:
Persons Arraymapping:Person mapping - willMapObjectFromRepresentation:
Person Dictionarymapping:Person mapping - willMapCollectionFromRepresentation:
Phones Arraymapping:Phone mapping - willMapObjectFromRepresentation:
Phone Dictionarymapping:Phone mapping - didMapObject:
Phone instancefromRepresentation:Phone Dictionarymapping:Phone mapping - didMapObject:
Person instancefromRepresentation:Person Dictionarymapping:Person mapping - didMapCollection:
Persons instances ArrayfromRepresentation:Persons Arraymapping:Person mapping
感谢
- 特别感谢lucasmedeirosleite提供的出色框架。
额外内容
阅读有关FastEasyMapping的博客文章。