DRBOperationTree 0.0.1
- 由
- Dustin Barker
DRBOperationTree 是 CocoaPods 上的一个 Objective-C/iOS 和 OSX API,用于将工作(NSOperations)组织成一个树,让每个父级的输出传递给其子级以进行进一步处理。
示例
让我们假设我们有一个 API,具有以下端点
| /cookbook/{cookbook_id} | 提供 recipe id 的列表 |
| /recipes/{recipe_id} | 提供 recipe 的 JSON 表示形式 |
| /ingredients/{ingredient_id} | 提供 ingredient 的 JSON 表示形式 |
| /images/{image_id} | 提供 PNG 图像 |
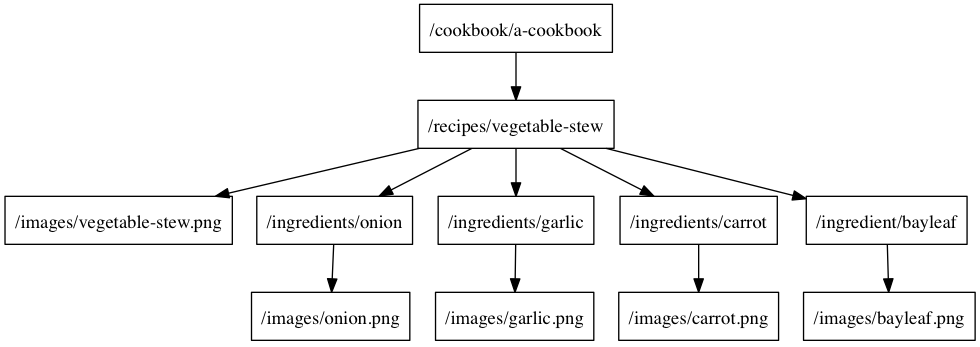
为了序列化 cookbook 的对象图,我们需要从 /cookbook/{cookbook_id} 端点获取 recipe id 的列表,然后获取每个 recipe,然后是每个 recipe 的每个图像和每个 ingredient。每个步骤中请求数取决于前一个请求的响应。例如,为了知道我们将要发起多少(以及多少个)/ingredients/{ingredient_id} 请求,我们必须首先获取并解析 /recipes/{recipe_id}/ingredient。我们可以将这些依赖关系建模为树。
如果我们需要对蔬菜炖菜 recipe 的对象图进行序列化,我们发起的请求树可能如下所示
假设我们正在开发一个 iOS 应用,它将在 cookbook 中显示所有 recipe。对于这个例子,主视图是一个包含图片和简短食材列表的 recipe 列表。为了显示 recipe,我们需要序列化 recipe 以及所有子对象。我们不想让用户在请求完成之前等待,所以让我们在 recipe 一旦准备好就显示给用户。这意味着我们将按层序遍历请求树,并在可能的情况下并行发起请求。我们可以尝试以下方法
[self fetchCookbook:cookbookID completion:^(id cookbook) {
for (id recipeID in cookbook.recipeIDs) {
[self fetchRecipe:recipeID completion:^{id recipe) {
for (id ingredientID in recipe.ingredientIDs) {
[self fetchIngredient:ingredientID completion:^(id ingredient) {
for (id imageID in ingredient.imageIDs) {
[recipe addIngredient:ingredient];
[self fetchImage:imageID completion:^(id image) {
[ingredient addImage:image];
}];
}
[recipe addIngredient:ingredient];
}];
}
}];
for (id imageID in recipe.images) {
[self fetchImage:imageID completion:^(id image) {
[recipe addImage:image];
}];
}
}
}];假设所有我们的获取方法都允许并发请求,这将实现我们的目标,但代码不是很理想。我们可以清理代码,但是还有一个问题需要解决:我们需要知道何时所有子对象都已序列化。在我们的请求树中,我们有两个叶节点集:recipe 图像和 ingredient 图像。在上面的方法中,我们需要添加代码来检测两组异步请求何时完成。
另一种方法会考虑到上述所有代码都遵循以下模式
- 将一个对象映射到一个或多个子对象(例如,cookbook -> recipes,recipe -> ingredients)
- 为每个子对象安排一些工作
DRBOperationTree 正确采取了这种方法。DRBOperationTree 允许我们将依赖关系定义为一个树,然后按照层级顺序执行每个节点对应的“工作”。当一个节点的所有后序遍历都完成时,该节点被标记为完成。以下是将上述代码重构为使用 DRBOperationTree 的方法。
DRBOperationTree *cookbook = [DRBOperationTree tree];
DRBOperationTree *recipe = [DRBOperationTree tree];
DRBOperationTree *recipeImage = [DRBOperationTree tree];
DRBOperationTree *ingredient = [DRBOperationTree tree];
DRBOperationTree *ingredientImage = [DRBOperationTree tree];
recipe.provider = [[RecipeProvider alloc] init];
recipeImage.provider = [[RecipeImageProvider alloc] init];
ingredient.provider = [[IngredientProvider alloc] init];
ingredientImage.provider = [[IngredientImageProvider alloc] init];
[cookbook addChild:recipe];
[recipe addChild:recipeImage];
[recipe addChild:ingredient];
[ingredient addChild:ingredientImage];
[cookbook sendObject:@"a-cookbook" completion:^{
// all done
}];树中的每个节点都将它的输出发送给它的子节点。在这个例子中,配方节点将序列化的配方对象发送给原料节点。ingredient.provider 负责将传入的配方对象映射到输出的原料对象。然后它创建 NSOperations,用于下载和序列化每个原料对象。提供者对象遵守 DRBOperationProvider 协议,该协议具有以下两个方法
// maps input objects to output objects (ex. recipe -> ingredient ids)
- (void)operationTree:(DRBOperationTree *)node
objectsForObject:(id)object
completion:(void(^)(NSArray *objects))completion {
// this method is optionally asynchronous
// in this example, we're just mapping a recipe to it's child ingredient ids
completion(recipe.ingredientIDs);
}
// given an object, returns an operation for that object and passes along the result
// (ex. ingredient id -> operation to fetch ingredient -> serialized ingredient object)
- (NSOperation *)operationTree:(DRBOperationTree *)node
operationForObject:(id)object
success:(void(^)(id object))success
failure:(void(^)())failure {
return [NSBlockOperation blockOperationWithBlock:^{
[self fetchIngredient:object completion:success];
}];
}使用 DRBOperationTree 的这种方法,我们
- 解决了最初的问题,并行序列化图以获得最佳用户体验
- 找到了一种方法来检测整个序列化是否完成(即当树的后续遍历完成时)
- 将外部代码重构为一个与我们的请求树相对应的结构
- 将内部代码重构为与我们的序列化每个步骤相对应的专业对象
维护者
许可证
DRBOperation 在 MIT 许可证下可用。有关更多信息,请参阅 LICENSE 文件。