ChainableAnimations 3.0.1
| 测试已测试 | ✓ |
| 语言语言 | Obj-CObjective C |
| 许可协议 | MIT |
| 发布上次发布 | 2017年10月 |
| SwiftSwift 版本 | 4.0 |
由 Jeff Hurray, Jeff Hurray 维护。
ChainableAnimations 3.0.1
- 作者:
- Jeff Hurray

|
|

|
|

|

|
3.x版本的新特性有哪些?
- 更简洁的语法
- 对Swift 4的支持
- 错误修正和改进
2.x版本的新特性有哪些?
- 从头重新架构,不再需要黑客UIView
🛠 - 为每个动画步骤添加了预动画和后动画钩子
⛓ - 添加了暂停和继续功能
⏯ - 添加了重复动画功能
🔂 - 在单独的框架中添加了友好的Swift接口
🔥 🕊
动画有什么问题?
CAAnimations和UIView动画非常强大,但很难将多个动画连接在一起,尤其是在改变锚点时。
此外,复杂的动画难以阅读。
比如说,我想将myView向右移动50像素,具有弹簧效果,然后当移动完成后,将背景颜色更改为了简化效果
旧方法
[UIView animateWithDuration:1.0
delay:0.0
usingSpringWithDamping:0.8
initialSpringVelocity:1.0
options:0 animations:^{
CGPoint newPosition = self.myView.frame.origin;
newPosition.x += 50;
self.myView.frame.origin = newPosition;
} completion:^(BOOL finished) {
[UIView animateWithDuration:0.5
delay:0.0
options:UIViewAnimationOptionCurveEaseIn
animations:^{
self.myView.backgroundColor = [UIColor purpleColor];
} completion:nil];
}];这太糟糕了... 使用JHChainableAnimations只需要一行代码。
使用JHChainableAnimations
JHChainableAnimator *animator = [[JHChainableAnimator alloc] initWithView:self.myView];
animator.moveX(50).spring.thenAfter(1.0).makeBackground([UIColor purpleColor]).easeIn.animate(0.5);当然也有很多好的动画库,比如RBBAnimation、DCAnimationKit和PMTween,但它们仍然无法提供强大的链式动画以及易于阅读/编写的语法。
安装
您可以将此框架添加到项目的几种方式中。Objective-C框架名为JHChainableAnimations,Swift框架名为ChainableAnimations。有关Swift使用的更多信息,请参阅此处
Objective-C
pod 'JHChainableAnimations', '~> 3.0.1'然后添加以下内容
#import <JHChainableAnimations/JHChainableAnimations.h>Swift
pod 'ChainableAnimations', '~> 3.0.1'然后添加以下内容
import ChainableAnimationsObjective-C
将JHChainableAnimations框架添加到项目中。
Swift
将ChainableAnimations框架添加到项目中。
手动添加到项目
您可以克隆仓库并将JHChainableAnimations中的文件手动添加。
使用方法
创建一个Animator实例
要创建一个JHChainableAnimator实例,您必须调用initWithView:方法。
JHChainableAnimator *animator = [[JHChainableAnimator alloc] initWithView:self.myView];动画
链式属性(如moveX(x))必须放在视图和animate(t)函数之间
以下是如何在一秒内将对象的大小翻倍的一个例子。
animator.makeScale(2.0).animate(1.0);组合动画
如果您想在缩放视图的同时移动视图,请添加另一个链式属性。顺序并不重要
animator.makeScale(2.0).moveXY(100, 50).animate(1.0);
// the same as animator.moveXY(100, 50).makeScale(2.0).animate(1.0);链式属性的完整列表可以在此处找到
链接动画
要链接动画,请使用thenAfter(t)函数分隔链。
以下是一个如何对物体进行放大0.5秒然后移动1秒的例子。
animator.makeScale(2.0).thenAfter(0.5).moveXY(100, 50).animate(1.0);动画效果
要添加动画效果,在要应用该动画的链式属性之后调用效果方法。
以下是一个使用弹簧效果的放大视图的例子。
animator.makeScale(2.0).spring.animate(1.0);如果您将2添加到相同的链式属性,第二个将取消第一个。
animator.makeScale(2.0).bounce.spring.animate(1.0);
// The same as animator.makeScale(2.0).spring.animate(1.0);完整的动画效果属性列表可以在这里找到
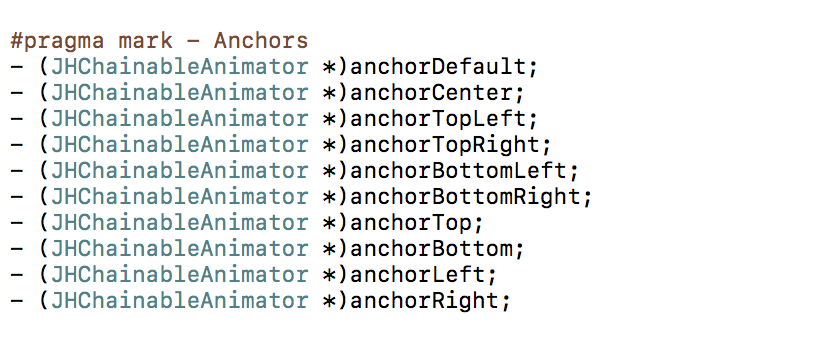
锚定
要在动画链中的某个点进行视图锚定,请调用锚定方法。就像效果一样,在相同链中一个接一个地调用将取消第一个。
以下是一个围绕不同锚点旋转视图的例子
animator.rotateZ(180).anchorTopLeft.thenAfter(1.0).rotateZ(90).anchorCenter.animate(1.0);
// animator.rotateZ(90).anchorTopLeft.anchorCenter == animator.rotateZ(90).anchorCenter完整的锚点属性列表可以在这里找到
延迟
要延迟动画,请调用wait(t)或delay(t)链式属性。
以下是在延迟0.5秒后移动视图的例子
animator.moveXY(100, 50).wait(0.5).animate(1.0);
// The same as animator.moveXY(100, 50).delay(0.5).animate(1.0);完成
要在动画完成后运行代码,请设置动画器的completionBlock属性或调用animateWithCompletion(t, completion)*函数。
animator.makeX(0).animateWithCompletion(1.0, ^{
NSLog(@"Animation Done");
});等同于
animator.completionBlock = ^{
NSLog(@"Animation Done");
};
animator.makeX(0).animate(1.0);重复动画
可以通过将thenAfter(time)方法替换为repeat(time, count)方法来重复动画。这将重复先前定义的动画。
// The animator will double its scale 3 times for 0.5 seconds each before it calls `moveXY` and finishes the animation
animator.makeScale(2.0).repeat(0.5, 3).moveXY(100, 50).animate(1.0);可以通过调用animateWithRepeat(time, count)来重复动画的最后一部分。
// The animator will double its scale then rotate by 90 degrees 3 times for 1 second each.
animator.makeScale(2.0).thenAfter(0.5).rotate(90). animateWithRepeat(1.0, 3);暂停和取消
要暂停动画,请在动画器上调用pause方法。当你调用暂停时,链中的当前动画将完成,但之后将不会有其他动作执行。您可以使用isPaused和isAnimating只读属性来检查状态。如果动画已暂停但未停止,它仍然会被视为animating。
要在一个暂停的状态下继续,请在动画器上调用resume方法。
要停止动画并清除状态,请在动画器上调用stop方法。
// In this case the `moveX` animation will execute but the `moveY` will not
// If `resume` is called `moveY` will be executed
// If `stop` is called, nothing will be executed and the animator will get a fresh state
animator.moveX(10).thenAfter(0.5).moveY(10).animate(0.5);
[animator pause];回调
您可以通过调用preAnimationBlock(block)、animationBlock(block)和postAnimationBlock(block)方法来挂钩到动画过程的各个步骤。所有这些方法都接受一个简单的块void(^)()作为参数。在动画链中调用这些方法的顺序不影响。
animator.moveX(10).preAnimationBlock(^{
NSLog(@"before the first animation");
}).thenAfter(1.0).postAnimationBlock(^{
NSLog(@"After the second animation");
}).moveY(10).animate(1.0);贝塞尔路径
您还可以在UIBezierPath上动画视图。创建一个UIBezierPath *实例,然后向其中添加点或曲线或线条,并在可链属性中使用它。
UIBezierPath *path = [UIBezierPath bezierPath];
[path moveToPoint:self.myView.center];
[path addLineToPoint:CGPointMake(25, 400)];
[path addLineToPoint:CGPointMake(300, 500)];
animator.moveOnPath(path).animate(1.0);动画效果不适用于路径移动。
与自动布局一起使用
变换
使用transform链式属性。这对于受自动布局约束的视图来说更好。您不应将这些属性与其他可链属性混合使用。
animatorForViewWithConstraints.transformX(50).transformScale(2).animate(1.0);与Swift一起使用
现在使用版本2.x的JHChainableAnimations与Swift的结合要容易阅读一些。我创建了一个用于Swift的单独框架,它提供了一个名为ChainableAnimator的类。这是一个对JHChainableAnimator的瘦包装器,它具有更易于阅读的语法。
let animator = ChainableAniamtor(view: myView)
animator.moveX(x: 50).thenAfter(t: 1.0).rotate(angle: 360).bounce.animate(t:1.0)所有Objective-C方法都映射到Swift方法。
可链属性
| 属性 | 接受... | 使用方法 |
|---|---|---|
| - (JHChainableRect) makeFrame; | CGRect | animator.makeFrame(rect).animate(1.0); |
| - (JHChainableRect) makeBounds; | CGRect | animator.makeBounds(rect).animate(1.0); |
| - (JHChainableSize) makeSize; | (CGFloat: width, CGFloat: height) | animator.makeSize(10, 20).animate(1.0); |
| - (JHChainablePoint) makeOrigin; | (CGFloat: x, CGFloat: y) | animator.makeOrigin(10, 20).animate(1.0); |
| - (JHChainablePoint) makeCenter; | (CGFloat: x, CGFloat: y) | animator.makeCenter(10, 20).animate(1.0); |
| - (JHChainableFloat) makeX; | (CGFloat: f) | animator.makeX(10).animate(1.0); |
| - (JHChainableFloat) makeY; | (CGFloat: f) | animator.makeY(10).animate(1.0); |
| - (JHChainableFloat) makeWidth; | (CGFloat: f) | animator.makeWidth(10).animate(1.0); |
| - (JHChainableFloat) makeHeight; | (CGFloat: f) | animator.makeHeight(10).animate(1.0); |
| - (JHChainableFloat) makeOpacity; | (CGFloat: f) | animator.makeOpacity(10).animate(1.0); |
| - (JHChainableColor) makeBackground; | (UIColor: 颜色) | animator.makeBackground(color).animate(1.0); |
| - (JHChainableColor) makeBorderColor; | (UIColor: 颜色) | animator.makeBorderColor(color).animate(1.0); |
| - (JHChainableFloat) makeBorderWidth; | (CGFloat: f) | animator.makeBorderWidth(3.0).animate(1.0); |
| - (JHChainableFloat) makeCornerRadius; | (CGFloat: f) | animator.makeCornerRadius(3.0).animate(1.0); |
| - (JHChainableFloat) makeScale; | (CGFloat: f) | animator.makeScale(2.0).animate(1.0); |
| - (JHChainableFloat) makeScaleX; | (CGFloat: f) | animator.makeScaleX(2.0).animate(1.0); |
| - (JHChainableFloat) makeScaleY; | (CGFloat: f) | animator.makeScaleY(2.0).animate(1.0); |
| - (JHChainablePoint) makeAnchor; | (CGFloat: x, CGFloat: y) | animator.makeAnchor(0.5, 0.5).animate(1.0); |
| - (JHChainableFloat) moveX; | (CGFloat: f) | animator.moveX(50).animate(1.0) |
| - (JHChainableFloat) moveY; | (CGFloat: f) | animator.moveY(50).animate(1.0) |
| - (JHChainablePoint) moveXY; | (CGFloat: x, CGFloat: y) | animator.moveXY(100, 50).animate(1.0) |
| - (JHChainableFloat) moveHeight; | (CGFloat: f) | animator.moveHeight(50).animate(1.0) |
| - (JHChainableFloat) moveWidth; | (CGFloat: f) | animator.moveWidth(50).animate(1.0) |
| - (JHChainableDegrees) rotateX; | (CGFloat: angle) #不是角度! | animator.rotateX(360).animate(1.0); |
| - (JHChainableDegrees) rotateY; | (CGFloat: angle) #不是角度! | animator.rotateY(360).animate(1.0); |
| - (JHChainableDegrees) rotateZ; | (CGFloat: angle) #不是角度! | animator.rotateZ(360).animate(1.0); |
| - (JHChainablePolarCoordinate) movePolar; | (CGFloat: radius, CGFloat: angle) | animator.movePolar(30, 90).animate(1.0); |
| - (JHChainableBezierPath) moveOnPath; | (UIBezierPath *path) | animator.moveOnPath(path).animate(1.0); |
| - (JHChainableBezierPath) moveAndRotateOnPath; | (UIBezierPath *path) | animator.moveAndRotateOnPath(path).animate(1.0); |
| - (JHChainableBezierPath) moveAndReverseRotateOnPath; | (UIBezierPath *path) | animator.moveAndReverseRotateOnPath(path).animate(1.0); |
| - (JHChainableFloat) transformX; | (CGFloat f) | animator.transformX(50).animate(1.0); |
| - (JHChainableFloat) transformX; | (CGFloat f) | animator.transformX(50).animate(1.0); |
| - (JHChainableFloat) transformY; | (CGFloat f) | animator.transformY(50).animate(1.0); |
| - (JHChainableFloat) transformZ; | (CGFloat f) | animator.transformZ(50).animate(1.0); |
| - (JHChainablePoint) transformXY; | (CGFloat x, CGFloat y) | animator.transformXY(50, 100).animate(1.0); |
| - (JHChainableFloat) transformScale; | (CGFloat f) | animator.transformScale(50).animate(1.0); |
| - (JHChainableFloat) transformScaleX; | (CGFloat f) | animator.transformScaleX(50).animate(1.0); |
| - (JHChainableFloat) transformScaleY; | (CGFloat f) | animator.transformScaleY(50).animate(1.0); |
| - (JHChainableAnimator *) transformIdentity; | 无 | animator.transformIdentity.animate(1.0); |
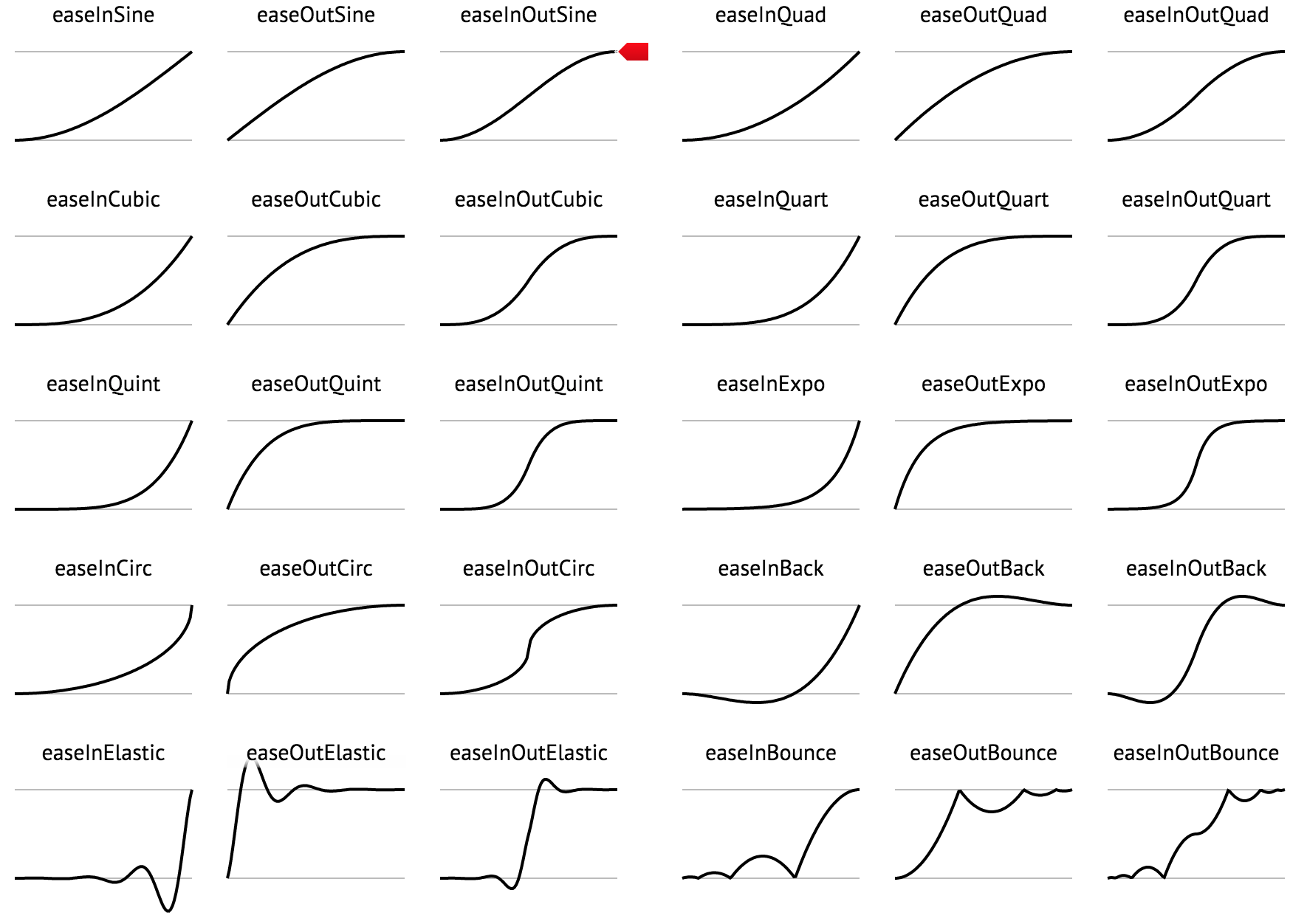
动画效果
有关这些函数的快速查阅可在此处找到here
这些动画函数来自一个很酷的键帧动画库,可在此处找到
它们基于可在此处找到的jQuery easing函数
锚定
有关锚定的信息可在此处找到here
待办事项
我已经收到了很多关于接下来做什么的极好的建议。如果您认为这里缺少任何东西,请告诉我!以下是我计划按照顺序工作的内容。
- OSX移植
- 约束动画器
联系信息 && 贡献
请随意通过[email protected]给我发邮件。我很乐意听到您的想法,或者看到已使用此技术的示例。